Content

For example, say you pay cash to purchase $5,000 of supplies and charge another $3,000 to your trade account. You debit the supplies T-account for $8,000, credit the cash T-account for $5,000 and credit the accounts payable T-account for $3,000.

The accounting equation balances because the company recorded equal amounts of debits ($550) and credits ($550). Thus, the company’s assets ($9,250) equal its total liabilities and stockholders’ equity ($9,250). In other words, the company’s accounting equation balances.
Why Cant Single Entry Systems Use T Accounts?
If the credit is due to a bill payment, then the utility will add the money to its own cash account, which is a debit because the account is another Asset. Again, the customer views the credit as an increase in the customer’s own money and does not see the other side of the transaction. When usingdouble-entry bookkeepingor the double-entry system, the debits and credits need to balance usually with an increase on one side and a decrease on the other. As you may assume, the accounting equation is central to thebalance sheetas it must always balance as well. You also have more money owed to you by your customers. You have performed the services, your customers owe you the money, and you will receive the money in the future. Debit accounts receivable as asset accounts increase with debits.
You made a purchase of gas on account earlier in the month, and at that time you increased accounts payable to show you had a liability to pay this amount sometime in the future. You are now paying down some of the money you owe on that account. Since you paid this money, you now have less of a liability so you want to see the liability account, accounts payable, decrease by the amount paid. As you can see, there is one ledger account for Cash and another for Common Stock. Cash is labeled account number 101 because it is an asset account type.
On the other hand, for a liability account or a shareholders’ equity, a debit entry on the left side results in a decrease to the account. In contrast, a credit entry on the right side increases to the account. If you add up the totals of the debits and credits in all four T-accounts, you will see that they balance. If you go even further, you will see that each debit entry has a corresponding credit entry. A double entry system is a detailed bookkeeping process where every entry has an additional corresponding entry to a different account. Consider the word “double” in “double entry” standing for “debit” and “credit”. The two totals for each must balance, otherwise there is an error in the recording.
don’t forget to earn & vote for jungwon on fanplus, too ! if you haven't created an account here's my referral codes #698a219e & #ab70b49a ! pic.twitter.com/uoQ9DX4ErZ
— miki (@jaygfrd) December 10, 2021
A credit decreases the balance of asset and expense accounts. For example, say the accounts receivables T-account balance is $1,000. If a customer pays $500 on his account, the $500 is credited to the accounts receivable account and reduces the balance to $500. However, a credit increases the balance of liability accounts, equity accounts and revenue accounts. For example, say the sales T-account balance is $2,000. If you have a $500 sale, you credit the $500 to the sales account, which increases the balance to $2,500. You enter a transaction’s debits in the left-hand side of the T-account.
What Is A T Account?
The asset account above has been added to by a debit value X, i.e. the balance has increased by £X or $X. Likewise, in the liability account below, the X in the credit column denotes the increasing effect on the liability account balance , because a credit to a liability account is an increase. When working with T-accounts andgeneral ledger accounts, the term contra account that will evidently come up. A contra account is an asset account there is a credit balance where the normal balance would be a debit. You paid, which means you gave cash so you have less cash.
’12 Hours I Can’t Account For’: Women Say Their Drinks Were Spiked at Maryland Bar – NBC4 Washington
’12 Hours I Can’t Account For’: Women Say Their Drinks Were Spiked at Maryland Bar.
Posted: Tue, 30 Nov 2021 08:00:00 GMT [source]
T-accounts can be a useful resource for bookkeeping and accounting novices, helping them understand debits, credits, and double-entry accounting principles. Unfortunately, any accounting entries that are completed manually run a much greater risk of inaccuracy. T-accounts are used as an aid for managing debits and credits when using double-entry accounting.
The above transaction would not only affect the Bank T account but also affect the contra account or second account, Capital. You have the following transactions the last few days of April. On January 14, 2019, distributed $100 cash in dividends to stockholders. On January 12, 2019, pays a $300 utility bill with cash. The first transaction to record would be the initial invoice for $4,000. Ms. Wilson is renting space in a strip mall for her bakery business from Mr. Jones. Ms. Wilson received an invoice on October 31st for $4,000 for October’s rent.
How Can An Accounts Payable T
Peruse Best Buy’s 2017 annual report to learn more about Best Buy. Take note of the company’s balance sheet on page 53 of the report and the income statement on page 54. These reports have much more information than the financial statements we have shown you; however, if you read through them you may notice some familiar items.

In this way, debits and credits increase or decrease the corresponding accounts to keep the books balanced. Another way to visualize business transactions is to write a general journal entry. Each general journal entry lists the date, the account title to be debited and the corresponding amount followed by the account title to be credited and the corresponding amount.
Sometimes you will see debit and credit labeled as dr and cr respectively. A useful tool for demonstrating certain transactions and events is the “t-account.” Importantly, one would not use t-accounts for actually maintaining the accounts of a business. Instead, they are just a quick and simple way to figure out how a small number of transactions and events will impact a company. T-accounts would quickly become unwieldy in an enlarged business setting. In essence, t-accounts are just a “scratch pad” for account analysis. They are useful communication devices to discuss, illustrate, and think about the impact of transactions.
Chapter 2: The Accounting Cycle
More detail for each of these transactions is provided, along with a few new transactions. The figures on your company’s financial statements tell only a small part of the story, even though they reflect the bigger picture. T-accounts and general ledger accounts use the same account titles and account numbers found on the chart of accounts. When you create a T-account, you place the account title and account number at the top of the T.
The balance sheet is one of the three fundamental financial statements. The financial statements are key to both financial modeling and accounting. Increase in shareholders equity account will be recorded via a credit entry. Increase in liability account will be recorded via a credit entry. Increase in a revenue account will be recorded via a credit entry. Increase in an expense account will be recorded via a debit entry.
Prepaid Rent Account
You have incurred more expenses, so you want to increase an expense account. Apr. 25You stop by your uncle’s gas station to refill both gas cans for your company, Watson’s Landscaping. 26You record another week’s revenue for the lawns mowed over the past week. 27You pay your local newspaper $35 to run an advertisement in this week’s paper.Apr. Accounts Receivable was originally used to recognize the future customer payment; now that the customer has paid in full, Accounts Receivable will decrease. Accounts Receivable is an asset, and assets decrease on the credit side.
T-accounts also provide a tool for helping to ensure that your entries will balance. No matter what type of accounting you are using, you can use a T-account as a visual aid in recording your financial transactions. T-accounts are called such because they are shaped like a T. Accounting Accounting software helps manage payable and receivable accounts, general ledgers, payroll and other accounting activities.
- The account title and account number appear above the T.
- Accountingverse is your prime source of expertly curated information for all things accounting.
- If the total amount of debits and credits do not balance, you should recheck all of the transactions to verify that you entered the amounts correctly.
- Example Of T AccountsThe T-Account is a visual representation of journal entries that are recorded in the general ledger account.
- The account title and account number identify which accounts are affected by a transaction.
- Debit balances are normal for asset and expense accounts, and credit balances are normal for liability, equity and revenue accounts.
- Banks like transaction deposits because they can avoid paying much, if any, interest on them.
As a smaller grocery store, Colfax does not offer the variety of products found in a larger supermarket or chain. Printing Plus provided the service, thus earning revenue. Salaries are an expense to the business for employee work. Expenses increase on the debit side; thus, Salaries Expense will increase on the debit side. This is a transaction that needs to be recorded, as Printing Plus has received money, and the stockholders have invested in the firm.
Format Of General Ledger
Dividends distribution occurred, which increases the Dividends account. Dividends is a part of stockholder’s equity and is recorded on the debit side. This debit entry has the effect of reducing stockholder’s equity. Paying a utility bill creates an expense for the company. Utility Expense increases, and does so on the debit side of the accounting equation.
When the company issues stock, stockholders purchase common stock, yielding a higher common stock figure than before issuance. The common stock account is increasing and affects equity. Looking at the expanded accounting equation, we see that Common Stock increases on the credit side. Once the rent is paid, accounts payable will be debited for $4,000, which will eliminate the liability, and cash will be credited for $4,000. Paying a salary of $4,000 will decrease his bank account balance.
Subsidiary Ledgers Or Sub Ledgers: Debtors Ledger And Creditors Ledger
Credits increase the balance of accounts that normally carry credit balances. Accounts with normal credit balances include gains, income, revenue, liabilities and stockholders’ or owners’ equity. For example, when a company buys a product from a vendor on credit, a bookkeeper records a credit to the company’s accounts payable account to reflect the liability. When the company pays its invoice for the product purchased on credit, the bookkeeper debits the accounts payable account to reflect that the company paid its liability.
Another key element to understanding the general ledger, and the third step in the accounting cycle, is how to calculate balances in ledger accounts. t account Recall that the general ledger is a record of each account and its balance. Reviewing journal entries individually can be tedious and time consuming.
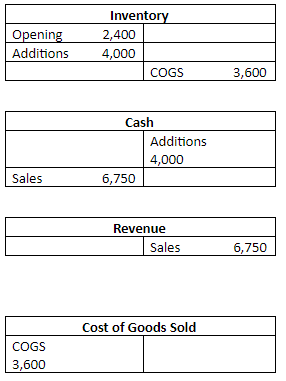
That is why each account has its own individual ledger account. For example, the fixed assets account would have its own ledger account with only transaction involving fixed assets.
The left column is for debit entries, while the right column is for credit entries. When we introduced debits and credits, you learned about the usefulness of T-accounts as a graphic representation of any account in the general ledger. But before transactions are posted to the T-accounts, they are first recorded using special forms known as journals. Using T-accounts lets you break down each step of an accounting transaction.